MUST READ: Information below is not medical advice. It is purely for educational purposes as sourced from CDC.gov. Information on this page MUST NOT be used to substitute advice from your doctor or be used to make medical decisions. Click on disease headers to go to latest CDC pages.
Tdap, HPV, MenACWY, MenB, Flu + COVID-19
Sars COV-2 (COVID-19 Vaccine)
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2) is the virus that causes COVID-19 (coronavirus disease 2019), the respiratory illness responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic. Although fewer children have been infected with COVID-19 compared to adults, children can:
- Be infected with the virus that causes COVID-19
- Get sick from COVID-19
- Spread COVID-19 to others
IMPORTANT - Per CDC's new guidelines released on June 6, 2025, the 2024-25 COVID-19 vaccine is recommended for most adults (< 18 YO). Parents of children & teens (6 months to 17 YO) should discuss the benefits of vaccination with a healthcare provider.
Human Papillomavirus (HPV Vaccine)
Human papillomavirus is a common virus. HPV is most common in people in their teens and early 20s. About 14 million people, including teens, become infected with HPV each year. HPV infection can cause cervical, vaginal, and vulvar cancers in women and penile cancer in men. HPV can also cause anal cancer, oropharyngeal cancer (back of the throat), and genital warts in both men and women.
The first opportunity for the HPV vaccine is at 9 years, 2 doses, 6-12 months apart.

Meningococcal Disease (Men ACWY, Men B Vaccines)
Meningococcal disease has two common outcomes: meningitis (infection of the lining of the brain and spinal cord) and bloodstream infections. The bacteria that cause meningococcal disease spread through the exchange of nose and throat droplets, such as when coughing, sneezing, or kissing. Symptoms include sudden onset of fever, headache, and stiff neck. With bloodstream infection, symptoms also include a dark purple rash. About one of every 10 people who gets the disease dies from it. Survivors of meningococcal disease may lose their arms or legs, become deaf, have problems with their nervous systems, become developmentally disabled, or suffer seizures or strokes.

Teens should also get a MenB shot, preferably at ages 16-18 years. Multiple doses are needed for best protection. More about the dangers of Meningitis B can be read here: https://meningitisbactionproject.org/about-meningitis
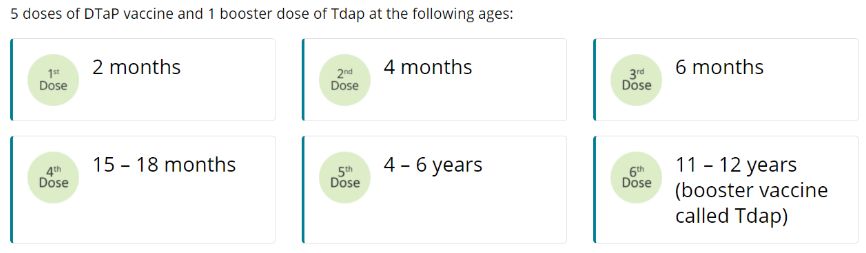
Diphtheria (Tdap Vaccine)
Diphtheria is a very contagious bacterial disease that affects the respiratory system, including the lungs. Diphtheria bacteria can be spread from person to person by direct contact with droplets from an infected person’s cough or sneeze. When people are infected, the bacteria can produce a toxin (poison) in the body that can cause a thick coating in the back of the nose or throat that makes it hard to breathe or swallow. Effects from this toxin can also lead to swelling of the heart muscle and, in some cases, heart failure. In serious cases, the illness can cause coma, paralysis, or even death.
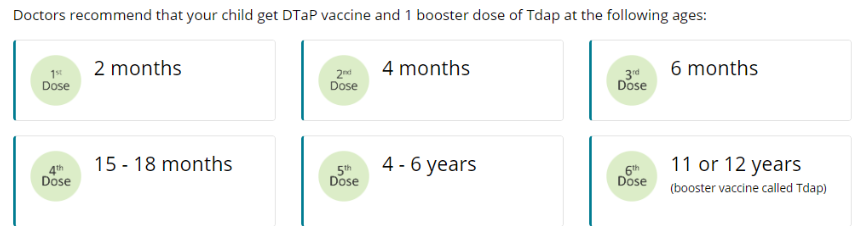
Tetanus, Lockjaw (Tdap Vaccine)
Tetanus mainly affects the neck and belly. When people are infected, the bacteria produce a toxin (poison) that causes muscles to become tight, which is very painful. This can lead to “locking” of the jaw so a person cannot open his or her mouth, swallow, or breathe. The bacteria that cause tetanus are found in soil, dust, and manure. The bacteria enter the body through a puncture, cut, or sore on the skin. Complete recovery from tetanus can take months. One to two out of 10 people who get tetanus die from the disease.
https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/parents/diseases/tetanus.html
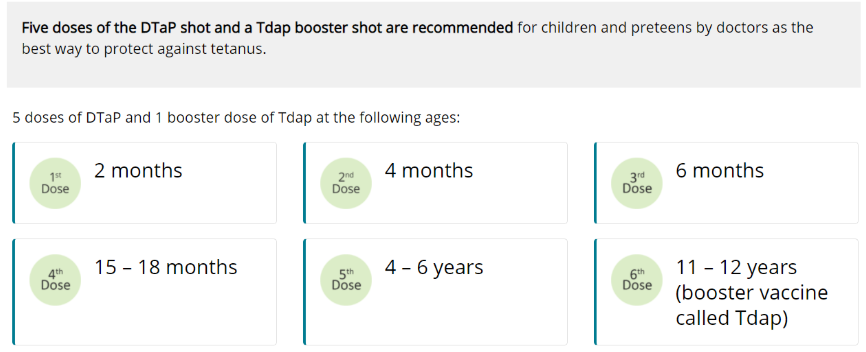
Pertussis, Whooping Cough (Tdap Vaccine)
Pertussis spreads very easily through coughing and sneezing. It can cause a bad cough that makes someone gasp for air after coughing fits. This cough can last for many weeks, which can make preteens and teens miss school and other activities. Pertussis can be deadly for babies who are too young to receive the vaccine. Often babies get whooping cough from their older brothers or sisters, like preteens or teens, or other people in the family. Babies with pertussis can get pneumonia, have seizures, become brain damaged, or even die. About half of children under 1 year of age who get pertussis must be hospitalized.
https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/parents/diseases/pertussis.html
Influenza (Flu Vaccine / Flu Nasal Spray)
Influenza is a highly contagious viral infection of the nose, throat, and lungs. The virus spreads easily through droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes and can cause mild to severe illness. Typical symptoms include a sudden high fever, chills, a dry cough, headache, runny nose, sore throat, and muscle and joint pain. Extreme fatigue can last from several days to weeks. Influenza may lead to hospitalization or even death, even among previously healthy children.
Yearly vaccine for flu is recommended
CHILDHOOD VACCINES - ARE YOU CAUGHT UP ON THESE?
Hepatitis A (HepA Vaccine)
Hepatitis A is an infection in the liver caused by hepatitis A virus. The virus is spread primarily person to person through the fecal-oral route. In other words, the virus is taken in by mouth from contact with objects, food, or drinks contaminated by the feces (stool) of an infected person. Symptoms can include fever, tiredness, poor appetite, vomiting, stomach pain, and sometimes jaundice (when skin and eyes turn yellow). An infected person may have no symptoms, may have mild illness for a week or two, may have severe illness for several months, or may rarely develop liver failure and die from the infection. In the U.S., about 100 people a year die from hepatitis A.

Hepatitis B (HepB Vaccine)
Hepatitis B causes a flu-like illness with loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, rashes, joint pain, and jaundice. Symptoms of acute hepatitis B include fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, pain in joints and stomach, dark urine, grey-colored stools, and jaundice (when skin and eyes turn yellow).
Measles (MMR Vaccine)
Measles is one of the most contagious viral diseases. Measles virus is spread by direct contact with the airborne respiratory droplets of an infected person. Measles is so contagious that just being in the same room after a person who has measles has already left can result in infection. Symptoms usually include a rash, fever, cough, and red, watery eyes. Fever can persist, rash can last for up to a week, and coughing can last about 10 days. Measles can also cause pneumonia, seizures, brain damage, or death.
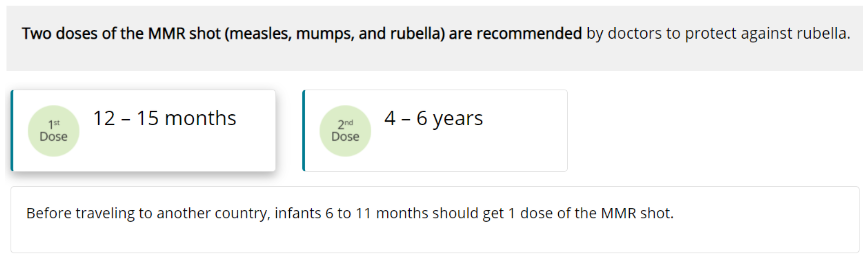
Mumps (MMR Vaccine)
Mumps is an infectious disease caused by the mumps virus, which is spread in the air by a cough or sneeze from an infected person. A child can also get infected with mumps by coming in contact with a contaminated object like a toy. The mumps virus causes swollen salivary glands under the ears or jaw, fever, muscle aches, tiredness, abdominal pain, and loss of appetite. Severe complications for children who get mumps are uncommon, but can include meningitis (infection of the lining of the brain and spinal cord), encephalitis (inflammation of the brain), permanent hearing loss, or swelling of the testes, which rarely results in decreased fertility.
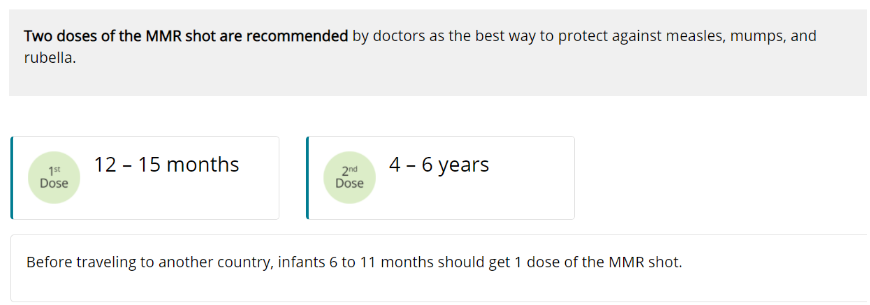
Rubella, German Measles (MMR Vaccine)
Rubella is caused by a virus that is spread through coughing and sneezing. In children, rubella usually causes a mild illness with fever, swollen glands, and a rash that lasts about 3 days. Rubella rarely causes serious illness or complications in children, but can be very serious to a baby in the womb. If a pregnant woman is infected, the result for the baby can be devastating, including miscarriage, serious heart defects, mental retardation, and loss of hearing and eyesight.
Two doses of the MMR shot (measles, mumps, and rubella) are recommended for children by doctors as the best way to protect against rubella. Before traveling to another country, infants 6 to 11 months should get 1 dose of the MMR shot.

Pneumococcal Disease (PCV13 Vaccine)
Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs that can be caused by the bacteria called “pneumococcus.” These bacteria can cause other types of infections, too, such as ear infections, sinus infections, meningitis (infection of the lining of the brain and spinal cord), and bloodstream infections. Sinus and ear infections are usually mild and are much more common than the more serious forms of pneumococcal disease. However, in some cases, pneumococcal disease can be fatal or result in long-term problems like brain damage and hearing loss. The bacteria that cause pneumococcal disease spread when people cough or sneeze. Many people have the bacteria in their nose or throat at one time or another without being ill—this is known as being a carrier.

Polio (Polio Vaccine)
Polio is caused by a virus that lives in an infected person’s throat and intestines. It spreads through contact with the stool of an infected person and through droplets from a sneeze or cough. Symptoms typically include sore throat, fever, tiredness, nausea, headache, or stomach pain. In about 1% of cases, polio can cause paralysis. Among those who are paralyzed, about 2 to 10 children out of 100 die because the virus affects the muscles that help them breathe.

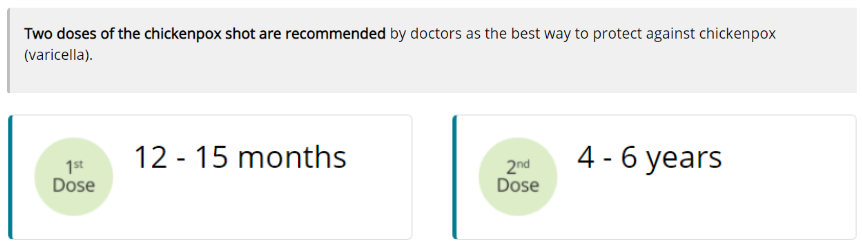
Varicella, Chickenpox (Varicella Vaccine)
Chickenpox is caused by the varicella zoster virus. Chickenpox is very contagious and spreads very easily from infected people. The virus can spread from either a cough or sneeze. It can also spread from the blisters on the skin, either by touching them or by breathing in these viral particles. Typical symptoms of chickenpox include an itchy rash with blisters, tiredness, headache, and fever. Chickenpox is usually mild, but it can lead to severe skin infections, pneumonia, encephalitis (brain swelling), or even death.
Play this game "Just Vax" from The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia to see how much you learnt!
REMINDER: The Information on this page is for educational purposes only. It must not be used to make medical decisions. Decisions about vaccinations, doses must be made with your doctor and not based on the information presented on this page.
Last updated: Apr 10, 2025